The EUDR (EU Deforestation free Regulation) was adopted by the European Union on May 16, 2023. This law aims to combat climate change through deforestation and forest degradation and focuses on the trade in timber, cattle, cocoa, coffee, palm oil, rubber, soy and derived products. The regulation will enter into force on December 30, 2024 and will therefore replace the EUTR.
The EU Deforestation Regulation, also known as “Regulation (EU) 2023/1115”, in addition to wood also focuses on cattle, cocoa, coffee, palm oil, rubber, soy and derivatives.
Main objectives of the EUDR are:
- stimulate demand for legal trade in “deforestation-free” raw materials and products within the EU
- minimizing the risk of products and raw materials linked to deforestation or forest degradation placed on or exported from the EU market.
The following questions are addressed below:
- Why this new EUDR regulation?
- From what date does the EUDR apply?
- Which raw materials are covered by the EUDR?
- Which HS codes are covered by the EUDR?
- What requirements does the EUDR impose?
- What are the requirements for Due diligence?
- What are the consequences of non-compliance with the EUDR?
- Where can I find the complete EUDR regulation?
- How current is this information?
Why this new EUDR regulation?
The European Union is a major consumer of products and raw materials associated with both deforestation and forest degradation.
Deforestation and forest degradation are major causes of climate change and loss of biodiversity, two important environmental challenges of our time.
On December 6, 2022, the EU reached an agreement on the new regulation: the EUDR", to prevent companies from using raw materials and products linked to deforestation and forest degradation placing on the EU market or exporting from the EU.
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) estimates that [420 million hectares of forest were lost to deforestation between 1990 and 2020](https: //www.fao.org/forest-resources-assessment/2020/en/).
From what date does the EUDR apply?
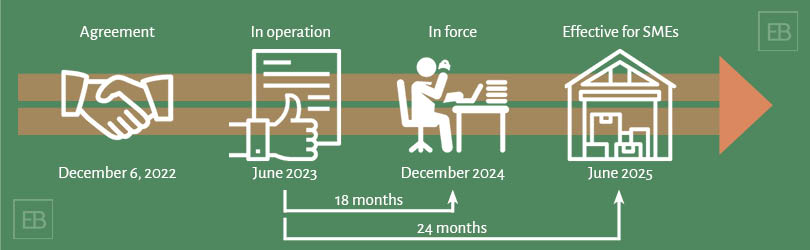
The EUDR regulation has been adopted and entered into force. The EUTR also applies for the next 3 years, depending on the time of felling.
The Cut off Date is set on December 31st, 2020. Timber harvested after that date must be demonstrably free from deforestation and forest degradation.
The EUDR will replace the EUTR on the date of application. The EUDR provides that timber and timber by-products (as listed in the EUTR) harvested before the date of entry into force and sold after the date of application are deemed to comply with the EUTR for 3 years.
Micro-enterprises (less than 10 FTE) have a transition period of 24 months to comply with the EUDR, but only for products that are not already covered by the EUTR.
Which raw materials are covered by the EUDR?
Regulation (EU) 2023/1115 has included 7 raw materials in the scope of the EU Regulation, namely:
- Cattle
- Cacao
- Coffee
- Palm oil
- Rubber
- Soy
- Wood
Within each raw material, the regulation defines which derivative products fall within the scope of the European regulation, through a list of HS codes.
The full list of all HS codes covered by the EUDR is shown below.
Which HS codes are covered by the EUDR?
The following are subject to the EUDR:
| Cattle | - 0102 21, 0102 29 - Live cattle
- 0202 - Meat from cattle, frozen
- 0206 10 - Edible offal of cattle, fresh or chilled
- 0206 22 - Edible offal of cattle, frozen livers
- 0206 29 - Edible offal of bovine animals (except tongues and livers), frozen
- 1602 50 - Other preparations or preserves of meat, offal or blood of bovine animals
- 4101 - Hides and skins of bovine animals, untanned (fresh, salted, dried, limed, pickled or otherwise preserved, but not tanned, processed into parchment or further prepared), whether or not depilated or split
- 4104 - Tanned hides and skins, hairless, and unfinished leather ("crust") of bovine animals, whether or not split, but not further processed
- 4107 - Leather further processed after tanning or drying, and hides and skins of bovine animals processed into parchment, without hair, whether or not split, other than products of heading 4114
|
| Cacao | - 1801 - Cocoa beans, even if broken, whether or not roasted
- 1802 - Cocoa shells, cocoa shells, cocoa husks and other cocoa waste
- 1803 - Cocoa paste, even if defatted
- 1804 - Cocoa butter, cocoa fat and cocoa oil
- 1805 - Cocoa powder, without added sugar or other sweeteners
- 1806 - Chocolate and other preparations for human consumption containing cocoa
|
| Coffee | - 0901 - Coffee, including decaffeinated coffee, whether or not roasted; husks and peels of coffee; coffee substitutes containing coffee, regardless of the mixing ratio
|
| Palm oil | - 1207 10 - Palm nuts and palm kernels
- 1511 - Palm oil and its fractions, whether or not refined, but not chemically modified
- 1513 21 - Crude palm kernel and babassu nut oil and their fractions, whether or not refined, but not chemically modified
- 1513 29 - Palm kernel and babassu nut oil and their fractions, whether or not refined, but not chemically modified (excluding crude oil)
- 2306 60 - Oilcake and other solid waste of palm nuts or palm kernels, obtained from the extraction of palm nut or palm kernel fats or oils, whether or not ground or in the form of pellets
- 2905 45 - Glycerol, with a purity of 95% (calculated on the weight of the dry product)
- 2915 70 - Palmitic acid and stearic acid, as well as their salts and esters
- 2915 90 - Saturated monovalent acyclic carboxylic acids, anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids derived therefrom; halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives thereof (excluding formic acid, acetic acid, mono-, di- and trichloroacetic acid, propionic acid, butanoic acid, pentanoic acid, palmitic acid, stearic acid, their salts and esters and acetic anhydride)
- 3823 11 - Industrial stearic acid
- 3823 12 - Industrial oleic acid
- 3823 19 - Fatty acids, industrial, monovalent; acid oils obtained from refining (excluding stearic acid, oleic acid and tall fatty acids)
- 3823 70 - Industrial fatty alcohols
|
| Rubber | - 4001 - Natural rubber, balata, gutta-percha, guyayule rubber, chicle and similar natural gums; in primary forms or in plates, sheets or strips
- 4005 - Prepared rubber, not vulcanized, in primary forms or in plates, sheets or strip
- 4006 - Unvulcanized rubber in other forms (e.g. bars, tubes and profiles) and articles thereof (e.g. discs and rings)
- 4007 - Wire and cord, made of vulcanized rubber
- 4008 - Plates, sheets, strips, rods and profiles, of non-hardened vulcanized rubber
- 4010 - Driving belts, driving belts and conveyor belts, made of vulcanized rubber
- 4011 - New pneumatic rubber tires
- 4012 - Used or retreaded pneumatic tires made of rubber; solid or semi-solid tyres, tire treads and rim strips, of rubber
- 4013 - Rubber inner tubes
- 4015 - Clothing and clothing accessories (including gloves, with or without fingers), for all purposes, of vulcanized rubber other than hard rubber
- 4016 - Other articles of unhardened vulcanized rubber, not elsewhere specified in Chapter 40
- 4017 - Hardened rubber (for example ebonite) in any form, including residues and waste; works of hardened rubber
|
| Soy | - 1201 - Soy beans, even if broken
- 1208 10 - Soybean flour
- 1507 - Soya oil and its fractions, whether or not refined, but not chemically modified
- 2304 - Oilcake and other solid residues resulting from the extraction of soya oil, whether or not comminuted or in the form of pellets
|
| Wood | - 4401 - Firewood, in the form of round or other logs, brushwood, bundles of branches and the like; wood in slices, chips or small pieces; sawdust, wood waste and scrap, whether or not agglomerated into logs, briquettes, pellets or similar forms
- 4402 - Charcoal (including charcoal obtained from fruit or nut shells), whether or not compressed
- 4403 - Wood, in the rough, whether or not stripped of bark, sapwood or simply cut into squares
- 4404 - Hoopwood; split stakes; posts and sticks of wood, pointed but not sawn lengthwise; wood, roughly worked or rounded, but not turned, bent or otherwise worked, for walking sticks, umbrellas, tool handles or the like; chipwood and wood in strips, ribbons and the like
- 4405 - Wood wool; wood flour
- 4406 - Wooden sleepers and switch timbers
- 4407 - Wood, sawn or chipped lengthwise, sliced or peeled, whether or not planed, sanded or end-jointed, of a thickness exceeding 6 mm
- 4408 - Veneer boards (including those obtained by cutting laminated wood), boards for the manufacture of plywood or plywood wood or similarly laminated wood, and other wood sawn lengthwise, sliced or peeled, whether or not planed, sanded, edge-jointed or longitudinally jointed, with a thickness not exceeding 6 mm
- 4409 - Wood (including non-assembled planks for parquet floors), at least one side or end of which is profiled (plowed, rebated, rounded with a V-joint or the like) over its entire length, whether or not planed, sanded or processed connected lengthwise
- 4410 - Chipboard, oriented strand board (OSB) and similar boards (for example waferboard), of wood or other wood-like materials, whether or not compressed with resins or other organic binding agents
- 4411 - Fibreboard of wood fibers or other woody fibres, whether or not bound with resins or other organic binding agents
- 4412 - Plywood and multiplex wood, veneer-coated wood and similarly laminated wood
- 4413 - Densified wood, in blocks, planks, strips or profiles
- 4414 - Wooden frames for paintings, photos, mirrors and the like
- 4415 - Packing boxes, crates, drums and similar packaging materials made of wood; cable reels of wood; pallets, loading boxes and other loading platforms, of wood; pallet collars, of wood (not packaging material used solely as packaging material to support, protect or carry another marketed product.)
- 4416 - Barrels, vats, tubs and other cooper's wares, and parts thereof, of wood, including staves
- 4417 - Tools, as well as tool frames and handles, brush handles, brush and broom handles, of wood; shoe lasts and shoe trees, made of wood
- 4418 - Joinery and carpentry for buildings, including cellular panels, assembled floor covering panels and shingles, of wood
- 4419 - Table and kitchen utensils made of wood
- 4420 - Wood inlay; cases, caskets and cases for jewelery or goldsmith's work, and similar articles, of wood; statuettes and other ornamental objects of wood; furniture making of wood, other than that of Chapter 94
- 4421 - Other wood products
- 47 & 48 - Wood pulp and paper of Chapters 47 and 48 of the Combined Nomenclature, excluding bamboo-based products and recovered (residual and waste) products
- 49 - Articles from the publishing house, the press or another graphic industry; written or typed texts and plans, made of paper
- 9401 - Chairs, benches and other seating furniture (other than those of heading 9402), whether or not convertible into beds, and parts thereof, of wood
- 9403 30, 9403 40, 9403 50, 9403 60 and 9403 91 - Wooden furniture and parts thereof
- 9406 10 - Prefabricated wooden buildings
|
What requirements does the EUDR impose?
Raw materials and products covered by the regulation may only be placed on the EU market or exported if:
- they are deforestation-free and not related to forest degradation,
- they are produced in accordance with the relevant legislation of the country of production,
- they are covered by a due diligence statement.
What are the requirements for Due diligence?
A key requirement of the EUDR is the obligation for operators and some traders to implement a due diligence system to avoid purchasing raw materials or products that are not deforestation-free, not linked to forest degradation or not produced in accordance with the relevant legislation of the country of production.
Companies that bring relevant raw materials onto the EU market or export them from the EU market are required to implement this due diligence system (DDS), risk analyses and mitigate non-negligible risks before placing them on the market or exporting them.
Companies described in the regulation as ’traders’ (trading goods already placed on the EU market) are responsible for storing and sharing information (with national competent authorities) about their supply chains.
However, large traders – who are not small to medium enterprises (SMEs) – will also need to conduct due diligence. This is due to their scale of influence in supply chains. They are also required to report publicly as broadly as possible annually on their due diligence systems and the steps they have taken to ensure they meet their obligations.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with the EUDR?
The consequences of non-compliance with the European Union Deforestation Free Regulation can be significant for companies. If a company does not comply with the requirements of the regulation, it may be confronted with legal and financial consequences. The EU can impose fines and trade restrictions on non-compliant companies.
For repeated serious violations, the fines are gradually increased. For a company, the maximum amount of such a fine is at least 4% of the total annual turnover in the previous financial year. If necessary, the maximum amount can be increased to ensure that the fine exceeds the possible economic benefit. It is likely that the products/commodities involved and the income earned from the products/commodities will be seized.
In cases of non-compliance, the costs of the authorities’ activities can be recovered from the companies (economic operators and traders).
These costs may include testing, warehousing and other activities associated with non-compliant products for which corrective action was taken before they were marketed, traded or exported.
In addition, the company’s image can be damaged, with negative consequences for brand value and consumer confidence.
How current is this information?
All this information has been compiled with the utmost care. Nevertheless, no rights can be derived from it. In addition, we do our best to update this page based on new information as it becomes available.



